Analysis of Class II deep overlap cases
- Age:14
- Gender:Female
- Chief complaint:dental irregularity
- Use product:PT V MBT
- Treatment cycle:1年
Analysis of Class II deep overlap cases
Basic patient information
Gender: Female
Age: 14
Medical history: None
Dental treatment history: None
Chief complaint: dental irregularity

Inspection&Diagnosis
1、Facial analysis


Frontal analysis Face type: oval
Symmetry: facial asymmetry
Chin: slightly to the right
Pupil connection: parallel
Corner line: parallel
Face ratio: 1/3 below the face is normal, and the upper and lower lip ratios are coordinated
Face protrusion: straight face type
Upper lip protrusion: normal
Lower lip protrusion: protrusion
Chin protrusion: normal
Chin neck angle: obtuse angle
Nasal chin labial angle

Nasolabial angle: 90 °
(Reference range: 90 ° - 95 °)
Chin lip angle: 118 °
(Reference range: 120 ° - 130 °)
Vertical line of the ideal anterior boundary of the upper jaw

Determine the target position in the natural head position;
The measured target distance from the initial FA point is - 1mm.
Lip tooth relationship
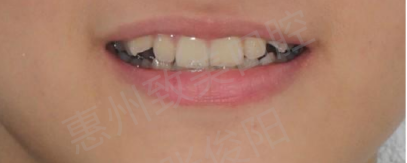
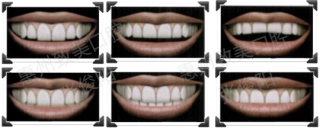
Tangent Curve: Flat
Smile Line: Medium
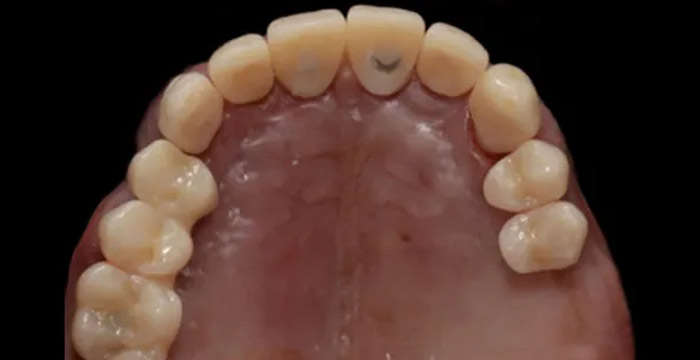
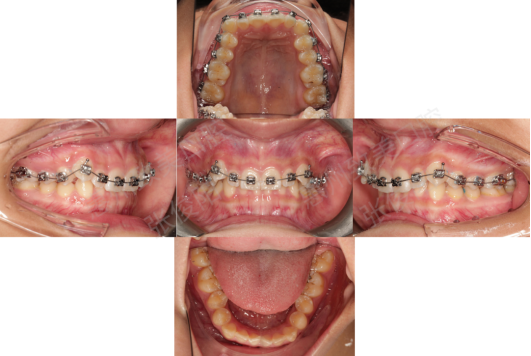
2、Intraoral analysis
Intraoral illumination
1. The maxillary and mandibular dental arches are basically symmetrical;
2. Upper jaw crowding is 4mm, lower jaw crowding is 2mm;
3.36, 46 Caries.
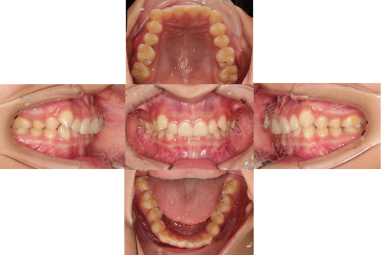
Horizontal relationship
The maxillary and mandibular dental arches are basically symmetrical

Vertical relationship
1. Third degree deep overlap of anterior teeth;
2.The speed curve is 3mm deep.
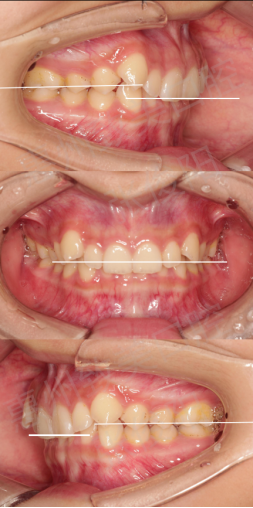
Forward and backward relationship
1. Slightly lingual inclination of lower anterior teeth;
2. Deep overlap of anterior teeth;
3. Molar relationship: completely distal;
4. Canine relationship: point-to-point.

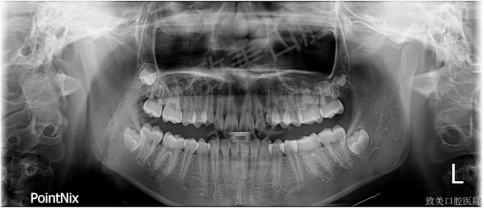
3. X-ray examination
Panorama
1. Teeth: 18, 28, 38, and 48 tooth germs exist, the root length is normal, and the periodontal membrane is normal;
2. Joint: The joint morphology is basically similar;
The maxillary sinus is slightly lower.
Cephalometric lateral radiograph
Normal airway
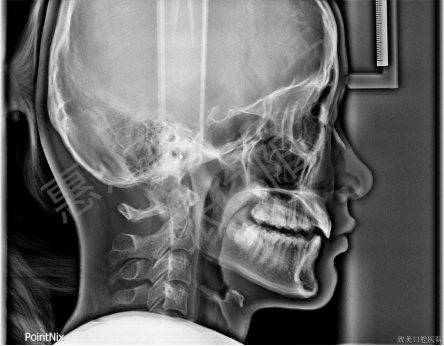
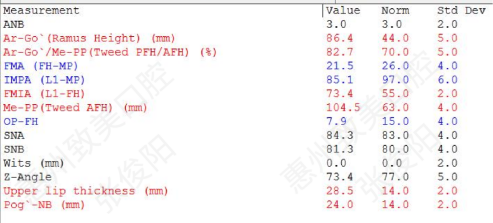
Analysis of cephalometric results:
4. Model Analysis
1. Molar relationship: completely distal;
2. Canine relationship: distal middle cusp;
3. Crowding degree: upper jaw crowding 4mm, lower jaw crowding 2mm;
4. Center line: the upper center line is aligned, and the lower center line is offset by 1mm to the left;
Bolton: anterior teeth 78.9%, complete teeth 91.9%.
5. Problems and Diagnosis
problem
1. Low angle;
2. Class II;
3. Third degree deep overlap of anterior teeth;
4. Crowded dentition;
5. The upper and lower front teeth incline slightly.
diagnosis
1. Bone type I;
2. Class II;
3. Uneven dentition.
6. Treatment goals and plans
Treatment goals
1. Maintain the face shape;
2. Control the inclination of the upper anterior teeth lip;
3. Align and level the upper and lower dentition;
4. Open the occlusion and establish normal maxillary coverage of the anterior teeth;
Establish a neutral relationship between molars and canines.
treatment planning
1. Implantation of anchorage nails in maxillary posterior teeth;
2. Move the maxillary posterior teeth far away;
3. Pute PT 5 self-locking bracket, low torque bracket alignment and leveling of upper and lower dentition;
4. Cooperate with Class II traction;
Establish a normal maxillary overlay of the anterior teeth, with a neutral molar and canine relationship.
Treatment process
9,5,2020
Adhesive maxillary bracket, 0.014 nt activation.
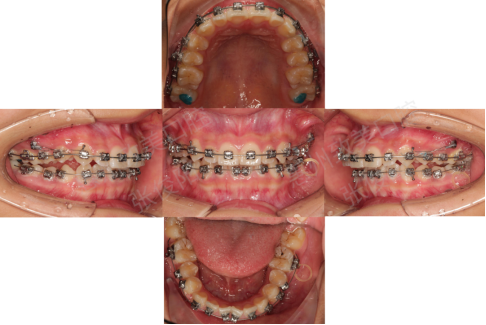
2020年11月7日
Maxillary replacement 0.016x0.022, distal maxillary movement bonding mandibular bracket 0.012nt activation, Class II traction hanging
.
3,13,2021
Maxillary displacement 0.017x0.025ss, distal maxillary displacement;
The mandible was replaced by 0.016 x 0.022 ss, with compression and low curvature.
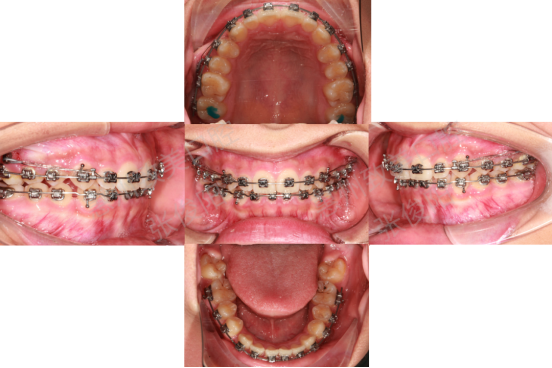
6,13,2021
Maxillary replacement 0.018x0.025ss;
Mandibular displacement 0.017x0.025ss.
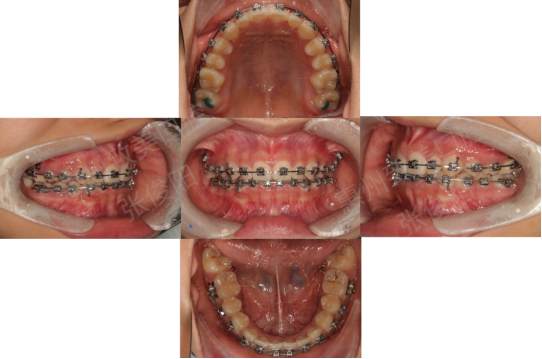
11,8,2021
End orthodontic treatment
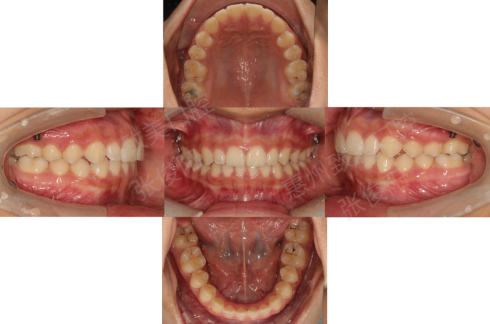
After treatment
1、Panorama Comparison
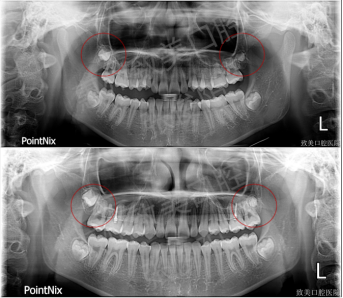
2. Comparison of cephalometric lateral films
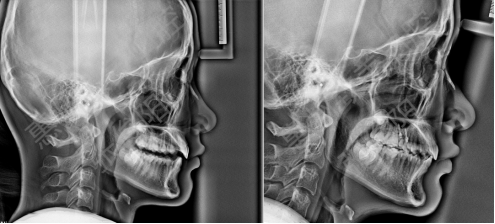
3. Intraoral contrast
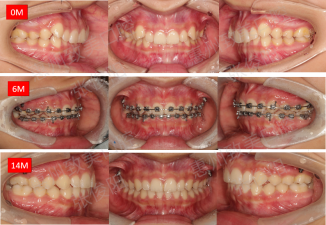
4. Facial contrast

Summary and experience sharing
1. Early implantation of anchorage nails and light force to move the maxillary posterior teeth far away is beneficial to providing space for the alignment of the anterior teeth, preventing the lip inclination of the aligned anterior teeth, thereby avoiding the reciprocating movement of the anterior teeth;
2. Pute low torque bracket effectively controls the lip inclination of the upper anterior teeth and maintains the existing face shape;
3. The distal displacement of the maxillary anchorage nail, combined with Class II traction, allows the molar to move from a completely distal to a neutral relationship;
4. Lower the upper anterior teeth and raise the posterior teeth to open the bite.
Last: Analysis of cases with deep coverage and deep curve
Next:empty
RELATED NEWS
-

-

-
 Tips On Choosing and Using Orthodontic Rubber Chainsnews | 2023-12-18
Tips On Choosing and Using Orthodontic Rubber Chainsnews | 2023-12-18
We are at your service.
Whether you have inquiries about our products or need assistance with troubleshooting, our team of sales and service experts is here to assist you.
GET A QUOTE