Non-extraction Orthodontics for Moderate Crowding
- Age:31
- Gender:Female
- Chief complaint:Protruding Mouth
- Use product:PT Clear Ceramic Self-ligating Brackets
- Treatment cycle:19 months
Examination:
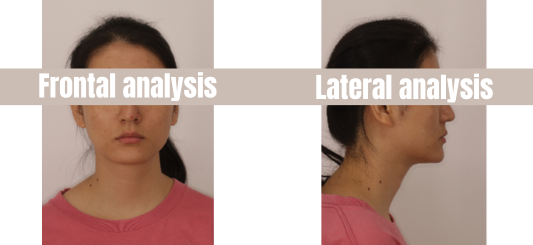
Facial Examination:
•Face shape: Oval•Symmetry: Facial asymmetry
•Chin: Normal
•Pupil line: Parallel
•Commissure line: Parallel
•Facial proportions: Lower third of the face slightly longer
•Facial convexity: Straight facial profile
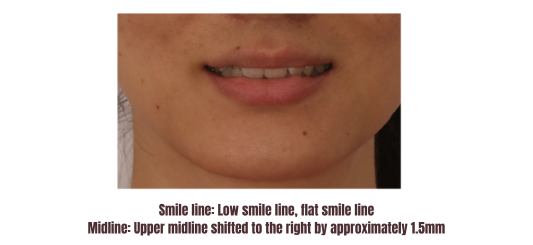
•Upper lip convexity: Retruded
•Lower lip convexity: Retruded
•Chin convexity: Prognathic
•Nasolabial angle: Right angle
•Mental crease: Soft
•Mental-cervical angle: Obtuse angle
Facial Examination:
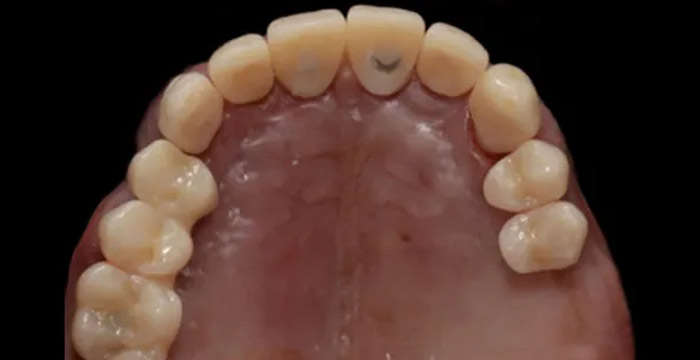
•Permanent teeth, 38 and 48, with proximal caries on the mesial aspect, and occlusal decay. Sinus tract noted in the apical region of tooth 14. Abnormal central cusps present on teeth 14, 34, and 44. (Intraoral examination)•Anterior crossbite with upper arch crowding of approximately 2mm and lower arch crowding of approximately 4mm. (Intraoral examination)
•Dental arches are round-shaped with narrow arch width. (Transverse relationship)
•Upper and lower dental arches show basic alignment. (Transverse relationship)
•Upper midline deviated to the right by approximately 1.5mm. (Transverse relationship)
•Occlusal planes are generally consistent. (Transverse relationship)
•Class I canine and molar relationship with normal overbite and even occlusal plane. Compensation curve and Spee's curve are normal. (Vertical relationship)
•Upper and lower anterior teeth inclined lingually. (Sagittal relationship)
•Class I canine relationship. (Sagittal relationship)
•Molar relationship in neutral occlusion. (Sagittal relationship)
•Class I relationship on the left side, and Class II relationship on the right side with mesial relationship of canines. (Sagittal relationship)
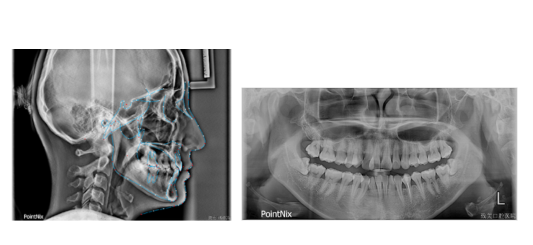
Cephalometric Examination:
•Permanent teeth, 38 and 48, with horizontal impaction of the mesial aspect. Low-density imaging noted in the apical region of tooth 14, and dense root canal filling observed in tooth 34.•Horizontal bone resorption in the alveolar bone.
•Maxillary sinus is relatively low.
•Temporomandibular joint: Joint morphology is generally similar.
Issues:
- Class III skeletal relationship.
- Crowded dental arches with some teeth in crossbite.
- Midline discrepancy.
- Lingual inclination of anterior teeth in both upper and lower jaws.
- Periapical cyst present at the apex of tooth 14.
- Impacted teeth 38 and 48.
- Retruded upper and lower lips, and prognathic chin.
Diagnosis:
•Angle Class I malocclusion.•Sagittal skeletal relationship: Class III.
•Vertical growth pattern: Average.
•Transverse width diagnosis: Rounded shape, narrow dental arch.
•Lip soft tissue position diagnosis: Retruded upper and lower lips.
•Midline: Upper midline deviated to the right.
•Crowding: Mild crowding in the maxilla, moderate crowding in the mandible.
•Others: Impacted teeth 38 and 48, periapical cyst at the apex of tooth 14, abnormal central cusp on tooth 44.
Treatment Progress:
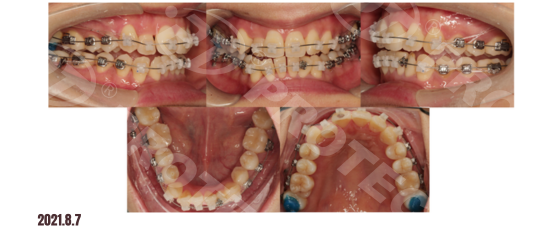
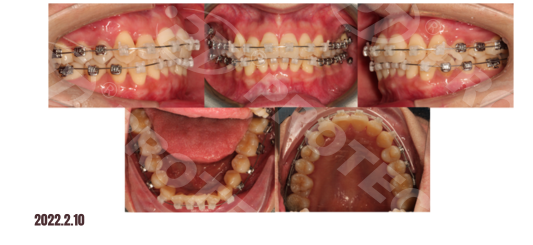
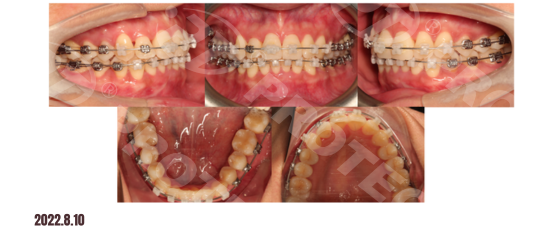
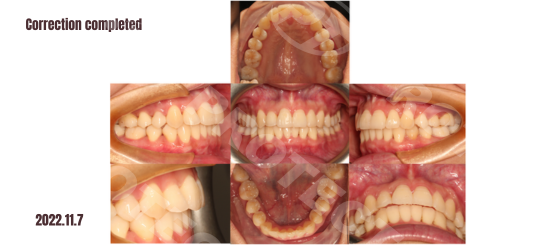
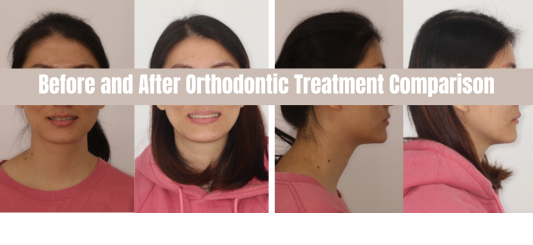
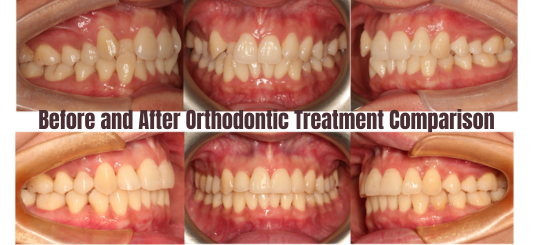
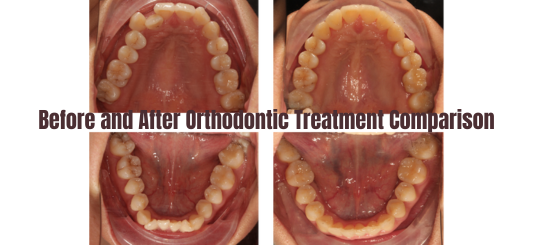
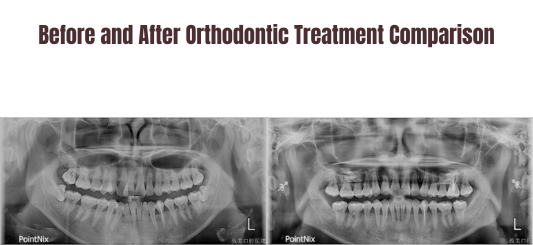
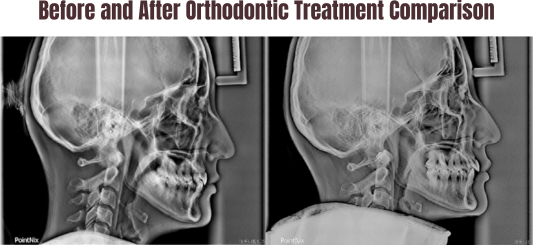
Summary:
Non-extraction orthodontic treatment for crowded teeth can utilize techniques such as interproximal enamel reduction, labial tooth inclination, and uprighting of molars to create space, thereby aligning the dental arches.
RELATED NEWS
-

-

-
 Tips On Choosing and Using Orthodontic Rubber Chainsnews | 2023-12-18
Tips On Choosing and Using Orthodontic Rubber Chainsnews | 2023-12-18
RELATED PRODUCT
RELATED case
-
 Treatment of Angle's Class I with Skeletal Class I Anterior Protrusion
Treatment of Angle's Class I with Skeletal Class I Anterior Protrusion
-
 Treatment of Class III Skeletal Malocclusion with Camouflage Techniques
Treatment of Class III Skeletal Malocclusion with Camouflage Techniques
-
 Orthodontic Treatment with Tooth Extraction for Mandibular Retrognathia
Orthodontic Treatment with Tooth Extraction for Mandibular Retrognathia
-
 Orthodontic Camouflage Treatment for Skeletal Class III Patient
Orthodontic Camouflage Treatment for Skeletal Class III Patient
-
 Analysis Of Class I Malocclusion with Bimaxillary Protrusion.
Analysis Of Class I Malocclusion with Bimaxillary Protrusion.
We are at your service.
Whether you have inquiries about our products or need assistance with troubleshooting, our team of sales and service experts is here to assist you.
GET A QUOTE