Treatment of Angle's Class I with Skeletal Class I Anterior Protrusion
- Age:21
- Gender:Female
- Chief complaint:protruding mouth
- Use product:PT V PLUS Self-ligating Brackets
- Treatment cycle:23.9 months
Issues:
Facial Examination:
Frontal view: Asymmetry of the face; skewed facial shape; lips parting to reveal teeth.
Lateral view: Convex profile; thick lips; deep mentolabial sulcus; sharp nasolabial angle.
1. Teeth 12 and 22 are undersized.
2. Misalignment of the midlines between the upper and lower jaws.
3. Deep overbite with the anterior teeth.
4. Severe crowding of the teeth in both the upper and lower arches.
5. Molar relationship is Angle's Class I.
Cephalometric Analysis:
1. Skeletal Class I.
2. Average angle.
3. Maxillary dental protrusion, lip inclination.
4. Soft tissue convexity.
Diagnosis:
Angle's Class I with skeletal Class I anterior protrusion.
Treatment Approach and Plan:
Treatment Objectives:
1. Adjust the profile soft tissues to align in a straight line.
2. Align and level the upper and lower dental arches.
3. Establish a normal overjet and overbite for the anterior teeth.
4. Adjust the molar relationship to Class I.
5. Align the midlines of the upper and lower jaws as closely as possible.
6. Retain the facial asymmetry.
Treatment Plan:
1. Extract teeth 14, 24, 34, 44.
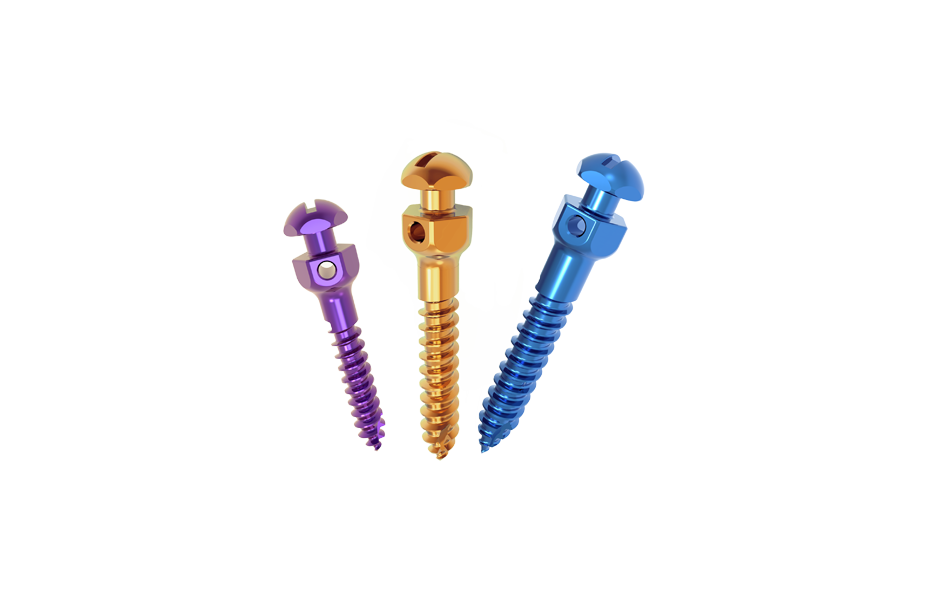
2. Place two anchorage screws in the upper jaw zygomatic alveolar ridge.
3. Wisdom teeth 18, 28, 38, 48 to be extracted at a later date.
4. The orthodontic treatment duration is about 2 years.
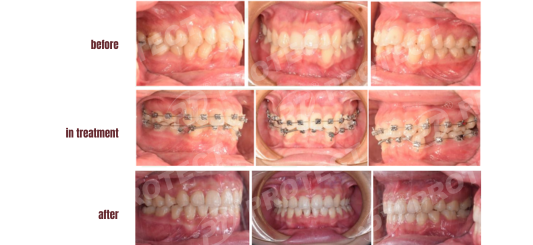
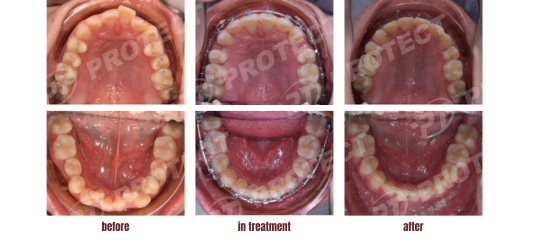
Treatment Progress:
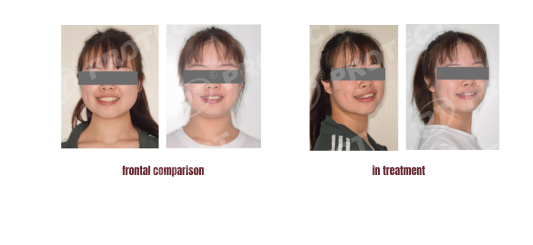
Summary:
1. For convex profile cases, the use of anchorage screws in the maxillary zygomatic alveolar ridge provides strong resistance for retraction, improving the side profile.
2. High torque brackets with long hooks and torque auxiliary arches are beneficial for controlling the root angulation during the retraction of the anterior teeth.
3. In cases of extraction with deep overbite and low angle, a flat guide can be used to open the vertical dimension of occlusion.
4. In cases with thick labial musculature, it is necessary to communicate with the patient before surgery to manage expectations and incorporate lip muscle training during treatment.
Last: Non-extraction Orthodontics for Moderate Crowding
Next: Treatment of Anterior Teeth in Crossbite with Posterior Teeth in Intercuspation
RELATED NEWS
-

-

-
 Tips On Choosing and Using Orthodontic Rubber Chainsnews | 2023-12-18
Tips On Choosing and Using Orthodontic Rubber Chainsnews | 2023-12-18
We are at your service.
Whether you have inquiries about our products or need assistance with troubleshooting, our team of sales and service experts is here to assist you.
GET A QUOTE